Aircraft investigation info>>>>>>> HOME PAGE
performance calculations for the Renault V8 WWI aero engine

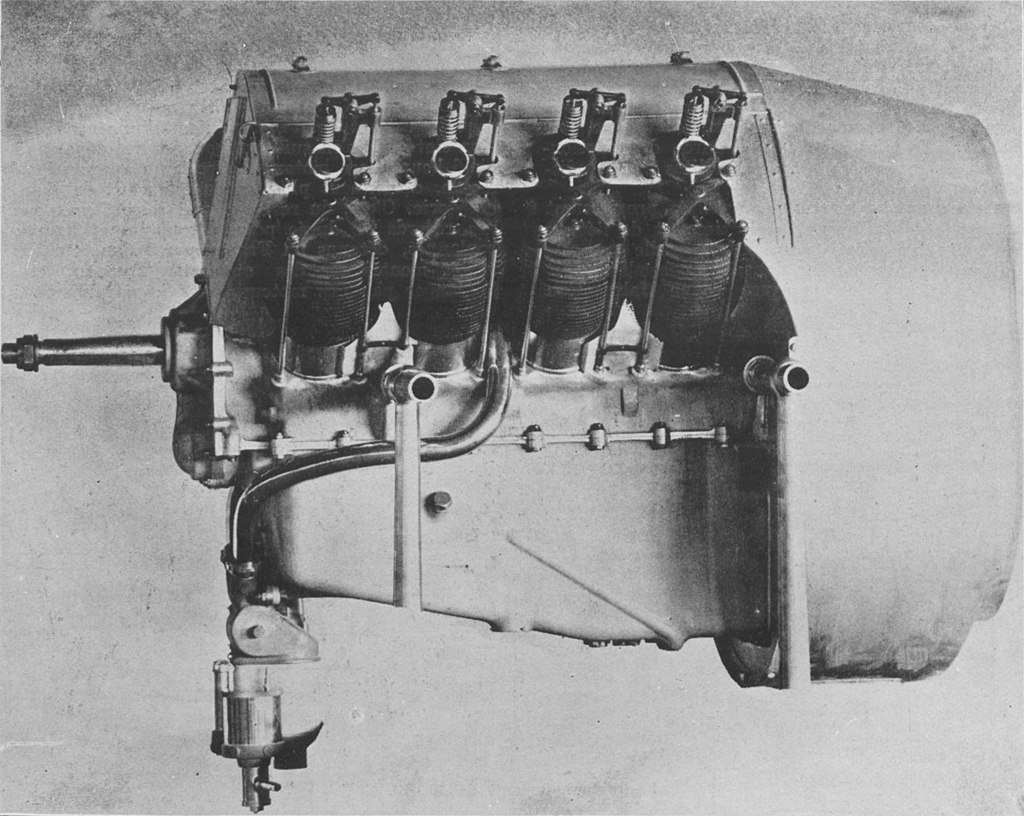
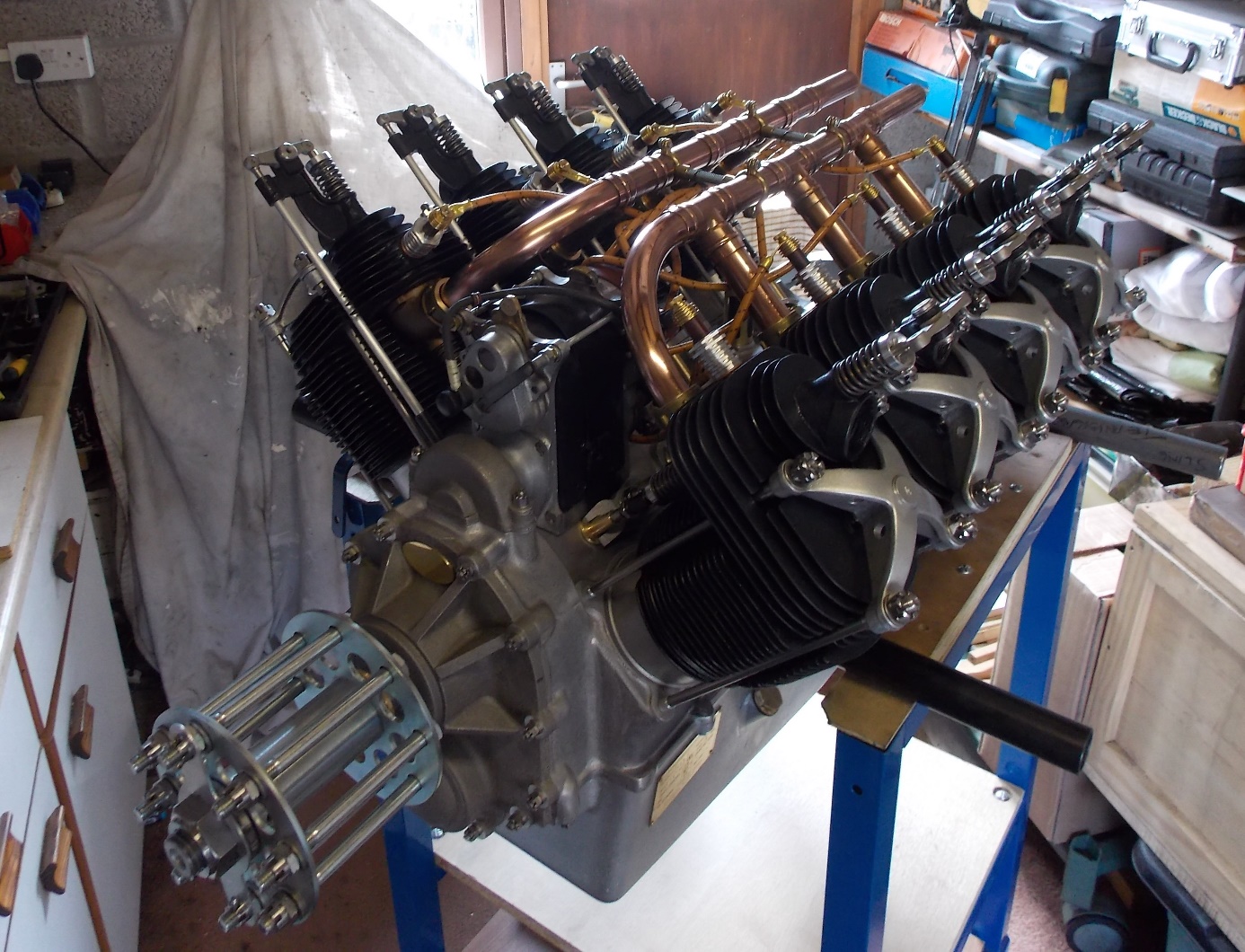
Renault V8 air-cooled 8 -cylinder V-engine 70 [hp](52.2 KW)
introduction : May 1913 country : France importance : ****
applications : Farman MF.7 Longhorn, RAF BE2a
max. continuous(take-off) rating : 70 [hp](52.2 KW) at 1750 [rpm] at 0 [m] above sea level
reduction : 0.5 , valvetrain : two side valves on lateral pocket
The Renault V-8 engines were noted as inefficient but reliable, the inefficiency being mainly due to the excessively rich fuel/air mixture used to assist cooling.
weight reduction gear : 2.1 [kg]
fuel system : single carburettor oil system :
weight engine(s) dry without reduction gear : 180.0 [kg] = 3.45 [kg/KW]
bore : 96.0 [mm] stroke : 120.0 [mm]
Mechanical efficiency/mean pressure correction factor : 0.661 [ ]
valve inlet area : 11.8 [cm^2] one inlet and one exhaust valve in cylinder head
gasspeed at inlet valve : 30.5 [m/s]
invloed hoogte > cm : 0.22 [ ]
rich mixture - additional cooling due fuel vaporizing
throttle : 99 /100 open, mixture :11.4 :1
compression ratio: 4.12 :1
calculated compression ratio : 4.12 : 1
published volume (displacement): 7.000 [litre]
calculated stroke volume (Vs) : 6.949 [litre]
compression volume (Vc): 2.227 [litre]
total volume (Vt): 9.176 [litre]
engine height : 82 [cm] engine width :79 [cm]
power / stroke volume (litervermogen Nl): 7.5 [kW/litre]

torque : 285 [Nm]
engine weight/volume : 25.7 : [kg/litre]
average piston speed (Cm): 7.0 [m/s]
***************************************************************************
intake pressure at 0 [m] altitude Pi : 0.99 [kg/cm2]
mean engine pressure (M.E.P.) at 0 [m] altitude Pm : 4.90 [kg/cm2]
compression pressure at 0 [m] altitude Pc: 5.73 [kg/cm2]
estimated combustion pressure at 0 [m] Pe : 21.78 [kg/cm2]
estimated combustion pressure at 0 [m] Pe : 22.88 [kg/cm2]
exhaust pressure at 0 [m] Pu : 3.66 [kg/cm^2 ]
**************************************************************************
compression-start temperature at 0 [m] Tic: 361 [°K] (88 [°C])
compression-end temperature at 0 [m] Tc: 495 [°K] (222 [°C])
caloric combustion temperature at 0 [m] Tec: 1880 [°K] (1606 [°C])
polytroph combustion temperature at 0 [m] Tep : 1882 [°K] (1608 [°C])
estimated combustion temperature at 0 [m] Te (T4): 1866 [°K] (1592 [°C])
polytrope exhaust temperature at 0 [m] Tup: 1291 [°K] (1018 [°C])
exhaust end temperature at 0 [m] Tu: 1198 [°K] (924 [°C])
*********************************************************************************
emergency/take off rating at 1768 [rpm] at sea level : 72 [hp]
Thermal efficiency Nth : 0.285 [ ]
Mechanical efficiency Nm : 0.680 [ ]
Thermo-dynamic efficiency Ntd : 0.194 [ ]
design hours : 2684 time between overhaul : 93
fuel consumption optimum mixture at 1750.00 [rpm] at 0 [m]: 31.54 [kg/hr]
specific fuel consumption thermo-dynamic : 310 [gr/epk] = 416 [gr/kwh]
estimated specific fuel consumption (cruise power) at 0 [m] optimum mixture : 435 [gr/kwh]
estimated sfc (cruise power) at 2000 [m] rich mixture : 485 [gr/kwh]
specific fuel consumption at 0 [m] at 1750 [rpm] with mixture :11.4 :1 : 604 [gr/kwh]
estimated specific oil consumption (cruise power) : 23 [gr/kwh]
Literature :
DISCLAIMER Above calculations are based on published data, they must be
regarded as indication not as facts.
Calculated performance and weight may not correspond with actual weights
and performances and are assumptions for which no responsibility can be taken.
Calculations are as accurate as possible, they can be fine-tuned when more data
is available, you are welcome to give suggestions and additional information
so we can improve our program. For copyright on drawings/photographs/
content please mail to below mail address
(c) B van der Zalm 24 June 2020 contact : info.aircraftinvestigation@gmail.com python 3.7.4